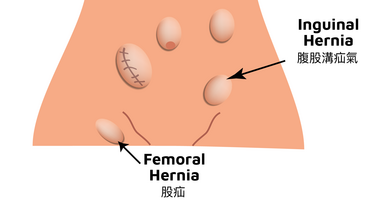
Hernia
Inguinal Hernia
HerniaHernias
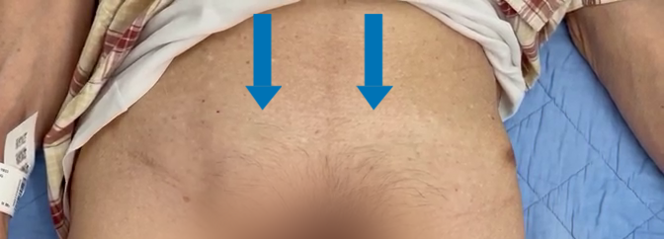
Bilateral inguinal hernia
Inguinal hernias are the most common type of abdominal wall hernia. It accounts for 75% of abdominal wall hernias and the chances of having a hernia is 27% in men and 3% in women. Surgery for
inguinal hernia is one of the most common operations in Hong Kong. Inguinal hernias occur more frequently in men and may be confined to one side or be present on both (bilateral). Patients with bilateral hernias may have them appear together or there may be a gap of several years before the second one becomes apparent.
Inguinal hernias usually present as a bulge in the groin. The bulge usually disappears when the patient lies flat and reappears after coughing or straining. Hernias usually occur when there is a cause of increase abdominal pressure. This can happen in patients suffering from certain conditions including benign prostatic hyperplasia, constipation, chronic cough and obesity. Sometimes, they can occur with heavy lifting. Diagnosis of the condition is usually made on examination by your doctor. Occasionally, radiological investigations may be required to help make the diagnosis
Treatment
While small, asymptomatic inguinal hernias can be safely observed. The natural progression however, typically involves enlargement of the hernia and development of symptoms over time. There are a number of possible ways to repair an inguinal hernia. This can be done by open and laparoscopic procedures. Studies have shown that laparoscopic repair is associated with better outcomes including lower risk of early and persistent pain after surgery, analgesic requirements and presence of foreign body sensation. Furthermore, it is the preferred approach in recurrent and bilateral hernias. However, laparoscopic repair needs to be done under general anaesthesia, so in patients that are at high risk for general anaesthesia, open repair may be preferred. The risk of recurrence in experienced hands is similar in both laparoscopic and open repair.
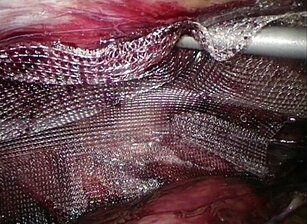
Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair
Laparoscopic repair of an inguinal hernia is performed through three small incisions measuring 5mm to 1 cm in size. The operation involves locating the hernia and placing a mesh that helps to repair the defect that is causing the hernia. In the open hernia repair, an incision approximately 6cm long is made in the groin. The hernia is identified and its contents are pushed back into the abdomen. A mesh is also placed to repair the defect that is causing the hernia. The operation can be performed under general or local anaesthesia. Both operations are offered at the CUHK Medical Centre Hernia Clinic. You can discuss with your doctor on which surgery is better suited for you.