Urology Centre
Service Hours
MON - FRI: 9:00AM - 5:00PM
SAT: 9:00AM - 1:00PM
SUN AND PUBLIC HOLIDAYS: CLOSED
Introduction
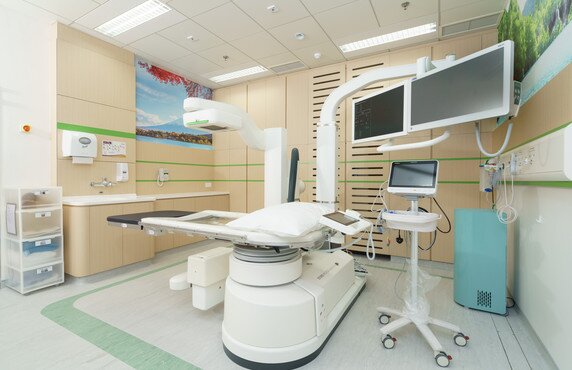
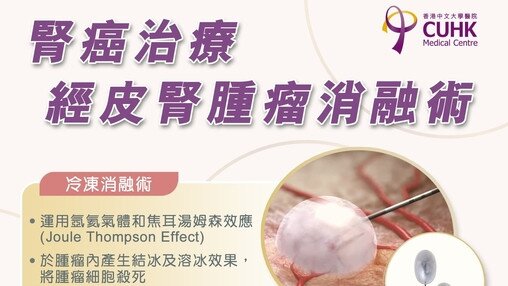
Dr and Mrs Tzu Leung Ho Urology Centre aims to provide professional urological assessment, diagnostic tests and therapies to patients. The centre is equipped with up-to-date equipment and supported by a team of urology specialists and nurses.
Our Services
- Uroflowmetry
- Urodynamic Study
- Cystoscopy
- Prostate Biopsy
- Extracorporeal Shockwave Lithotripsy
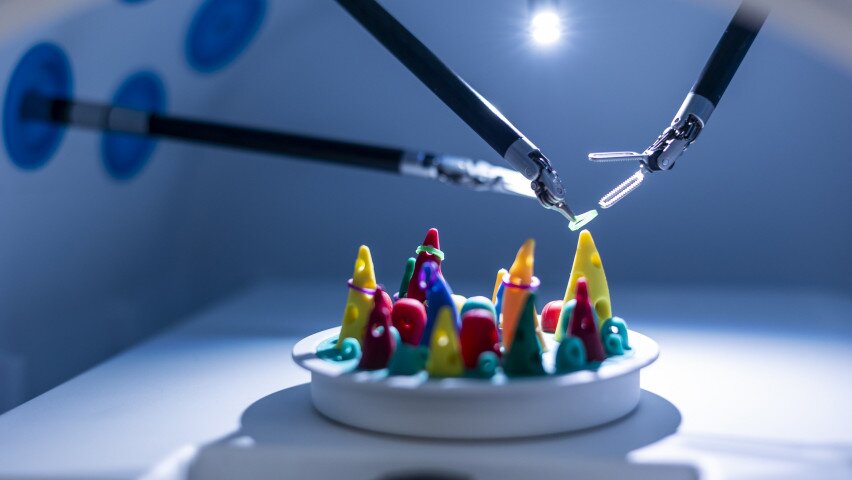
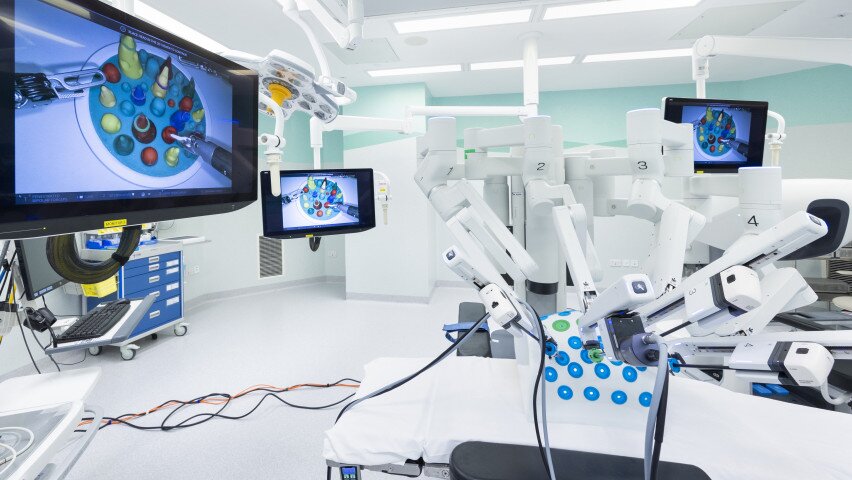
- Robotic Surgery
- Urology Nursing Service
Fees and Packages
Download
Feature Articles
View AllHealth Knowledge
View AllMedical Team
View AllCUHK Professorial Team
CUHKMC Medical Team

 View Profile
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Clinical Associate Professor (honorary), Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, CUHK
 View Profile
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology

Dr NGO Chang Chung
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Clinical Assistant Professor (honorary), Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, CUHK
Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, LKS Faculty of Medicine, HKU

Dr CHAN Shu Yin, Eddie
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Service Hours
MON - FRI: 9:00AM - 5:00PM
SAT: 9:00AM - 1:00PM
SUN AND PUBLIC HOLIDAYS: CLOSED
Explore Medical Team