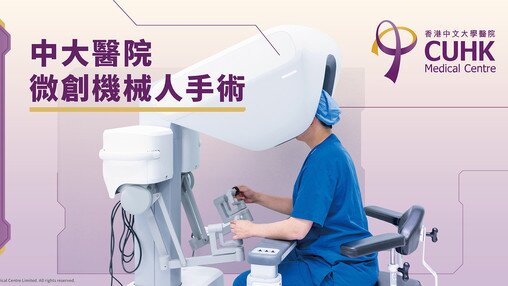
Urology
Introduction
Our Urologist cover different subspecialties within Urology and offer professional assessment and suitable treatment for various urological problems.
Our Services
Our Centres and Clinics
Diseases to be seen
- Urological cancer
- Prostate / Bladder / Kidney / Testicular / Penile cancer
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Voiding dysfunction / urinary incontinence
- Urinary tract infection / Haematuria
- Urinary stone diseases
- Men’s health services
Investigations in Urology Center
- Urinalysis
- Uroflowmetry
- Urodynamic studies
- Ultrasound kidney, prostate, scrotum
- Bladder volume assessment
Day / Office procedures
- Flexible cystoscopy
- Transperineal prostate biopsy
- MRI-ultrasound fusion prostate biopsy
- Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy
- Circumcision
- Vasectomy
In-patient treatment & operative procedures
- Urological cancer surgery (Open / Minimally invasive)
- Transurethral resection of bladder tumour
- Transurethral resection of prostate (monopolar / bipolar / Laser)
- Water vapour thermal therapy of the prostate
- Endoscopic stone surgery
- Scrotal / penile surgery
- Hernia repair
Fees & Packages
Feature Articles
View AllHealth Knowledge
View AllMedical Team
View AllCUHK Professorial Team
CUHKMC Medical Team

 View Profile
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Clinical Associate Professor (honorary), Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, CUHK
 View Profile
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology

Dr NGO Chang Chung
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Clinical Assistant Professor (honorary), Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, CUHK
Honorary Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, LKS Faculty of Medicine, HKU

Dr CHAN Shu Yin, Eddie
View Profile- Consultant
- Specialist in Urology
Explore Medical Team