GI Disease
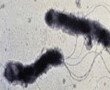
Helicobacter pylori Infection
GI DiseaseEsophagus and Stomach
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a bacterium found in the stomach and duodenum. It can cause mild chronic inflammation of the gastric mucosa, or even lead to gastric and duodenal ulcers or gastric cancer. About 30% - 50% of the world population is estimated to have detectable H. pylori in their gastrointestinal tract. Most individuals infected with H. pylori have few or no symptoms. They may experience a few episodes of gastritis (minor belching, bloating, nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort). Accurate and simple tests for the detection of H. pylori infection are available. They include blood antibody tests, urea breath tests, stool antigen tests, and endoscopic biopsies. Once H. pylori is detected in a person, a course of eradication treatment consisting of proton pump inhibitors and the antibiotics will be prescribed. About ninety percent of those who take on the full course of treatment are cured.